Snort IDS – Part 01: Installing Snort

Welcome Back!
Snort remains one of the most widely encountered intrusion detection systems (IDS) in modern security environments. If you have ever worked with traditional antivirus (AV) software on an endpoint, the concept is similar. Instead of scanning files on a machine, Snort analyzes network traffic and notifies you when it identifies signatures or behaviors associated with malicious activity. It is a foundational tool to understand for anyone developing defensive skills or working within network security.
Snort was originally developed by Martin Roesch in 1999. Its adoption grew rapidly, and in 2014 Cisco acquired it, integrating Snort into many of their security appliances and platforms. Because Cisco maintains a significant presence across enterprise networks, there is a strong probability that you will encounter Snort directly or indirectly throughout your cybersecurity journey.
Even if your organization does not deploy Snort or Cisco solutions, understanding Snort’s architecture remains valuable. Many IDS and IPS technologies are built on similar principles, and Snort provides a clear and accessible foundation for learning modern network detection practices.
This article begins a complete series on Snort 3, the updated and actively maintained version of the Snort IDS engine. In this first part, we focus entirely on installing Snort 3 on Kali Linux using two different methods.
Method 1: Installing Snort 3 from the Repositories
Snort installation is straightforward when your distribution provides it in its repositories. Recent versions of Kali Linux include Snort 3 directly, which allows installation without modifying any external sources.
To begin, update your package lists:
sudo apt-get update
After the update completes, install Snort 3:
sudo apt-get install -y snort3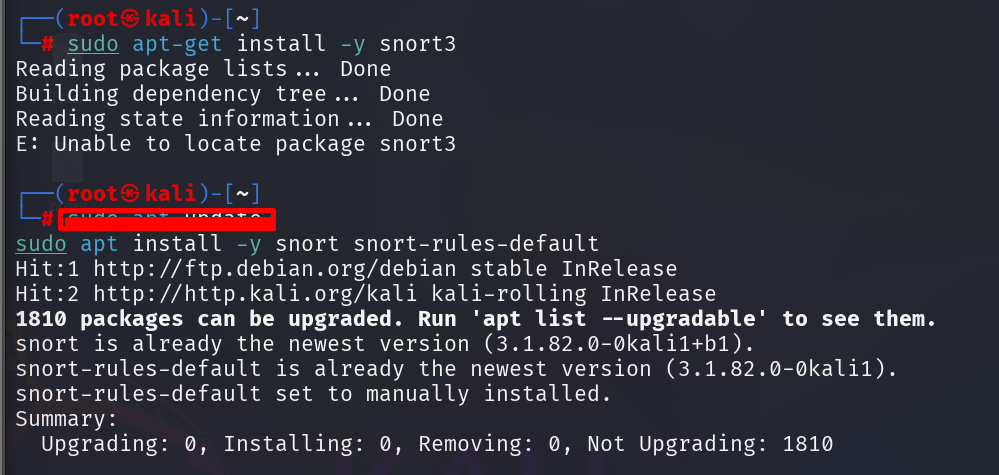
You can verify the installation and check Snort’s version number:
snort3 -V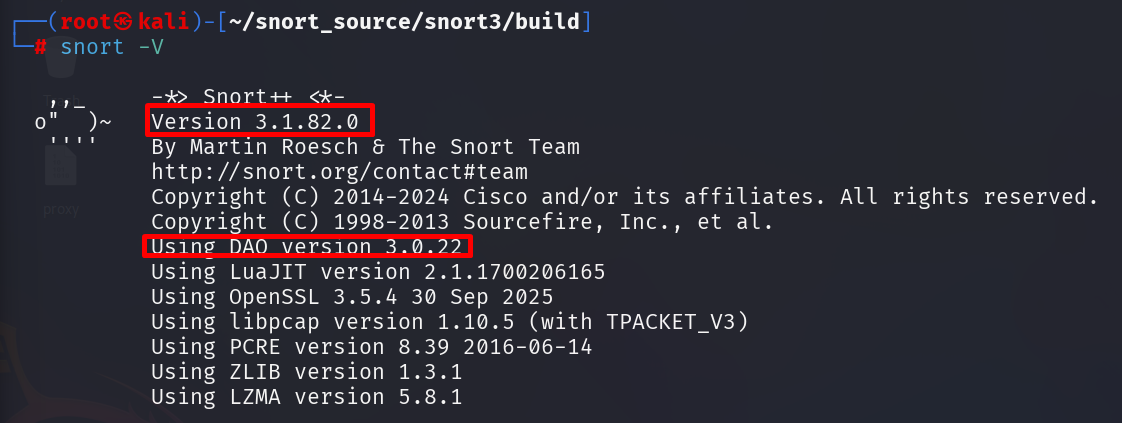
Snort 3 is now installed and ready for use. This method is fast and effective for learning, testing, and general experimentation. However, for environments where performance, customization, or the most recent updates are essential, installing Snort from source remains the preferred method.
Method 2: Installing Snort 3 from Source
Installing Snort 3 from source requires more steps, but it provides significant advantages. Compiling Snort specifically for your system’s architecture often results in better performance. Performance matters greatly in IDS systems because the engine must process traffic quickly and consistently. Performance issues can slow down the network or cause packet loss, and both outcomes negatively affect detection accuracy.
Source installation also ensures that you are working with the most recent Snort 3 version, which may include updates not yet available through distribution repositories.
We will begin by preparing a working directory for Snort’s source files.
1. Create a Directory for Snort Source
Create a workspace:
mkdir snort_sourceNavigate into it:
cd snort_source
2. Install Required Build Dependencies
Snort 3 has several development dependencies that must be installed before compiling from source. Install them with the following command:
sudo apt-get install -y build-essential cmake pkg-config \
libpcap-dev libpcre3-dev libdnet-dev zlib1g-dev \
libluajit-5.1-dev libssl-dev libhwloc-dev \
libnetfilter-queue-dev libmnl-dev autoconf automake libtool git
3. Download and Install the Modern DAQ Library
Snort 3 uses the updated Data Acquisition (DAQ) library, maintained on GitHub. Download the source:
git clone https://github.com/snort3/libdaq.gitEnter the directory:
cd libdaqPrepare and configure the DAQ build environment:
./bootstrap
./configureCompile and install DAQ:
make
sudo make install
Return to your main source directory:
cd ..4. Download Snort 3 Source Code
Download the official Snort 3 repository:
git clone https://github.com/snort3/snort3.gitNavigate into the Snort directory:
cd snort3
5. Configure and Build Snort 3
Configure Snort using the official script:
./configure_cmake.sh --prefix=/usr/local/snort3Move into the build directory:
cd buildCompile Snort:
makeInstall Snort:
sudo make install
6. Update Shared Libraries
Because new libraries were installed during this process, update the system’s shared library cache:
sudo ldconfig
7. Create a Symlink for Convenience
To run Snort 3 globally from any directory, create a symbolic link:
sudo ln -s /usr/local/snort3/bin/snort /usr/sbin/snort3
8. Test the Snort 3 Installation
Validate the installation:
snort3 -VSnort should display its version information along with DAQ details.

Snort is now installed successfully and ready for configuration.
With Snort installed, we will next focus on configuring the system so that it can begin analyzing traffic and detecting malicious activity. The next article in this series will guide you through rule loading, network variables, and essential configuration steps.
Stay Curious!